There are many ways to reduce energy consumption in a home. Some go for turning off the light once you leave a room, unplugging unused appliances, adjusting thermostat settings, etc. While these are proven ways, they are less effective than regular home insulation.
A study shows that insulating a home is one of the most effective ways to save energy and, in turn, reduce the home’s annual utility bills. Insulation can be done with various materials; each has advantages and disadvantages.
In this article, I will discuss home insulation, how it works, the various materials that can be used, and which is best. So, let’s dive right into it without taking much of your time.
What is home insulation?

To fully grasp the concept of home insulation, it is important to understand heat flow first. Heat flow involves three processes: conduction, convection, and radiation.
Conduction is how heat travels through a material, convection is how heat moves through liquid and gas, and radiation is how heat travels through waves and warms up whatever it hits, just like the sun.
Insulation is simply a material used in a building to stop or reduce energy and heat flow regardless of the process of heat transfer. This material reduces heat loss or gain by providing a barrier between inside and outside temperatures. Therefore, home installation is done when an insulation material reduces heat loss within the home.
Why is home insulation important?
Insulation plays so many roles in the home today. A properly insulated home will keep the desired temperature in your home all year round, protecting you from cold in the winter and heat in the summer. Home insulation also stops or limits heat transfer from inside your home to the outside as much as possible. Additionally, it helps in reducing noise pollution in the home.
Types of home insulation
There are various types of insulation, each with pros and cons. They include;
1. Blankets (batts and rolls) insulation
Blankets insulation consists of various materials, such as; fiberglass, natural fibers, mineral wool, and plastic fibers. However, the most common type of material used is fiberglass. This type of installation is fitted between studs, joists, and beams. It is best suited for unfinished walls, including foundation walls, floors, and ceilings.
Advantages
- Inexpensive
- Very easy installation
- Reduces noise from outside and acts as a sound barrier between floors and rooms in the home
Disadvantages
- Any form of adjustment will result in compression and may reduce the effectiveness
- Low R-Value (the higher the R-Value, the higher the effectiveness)
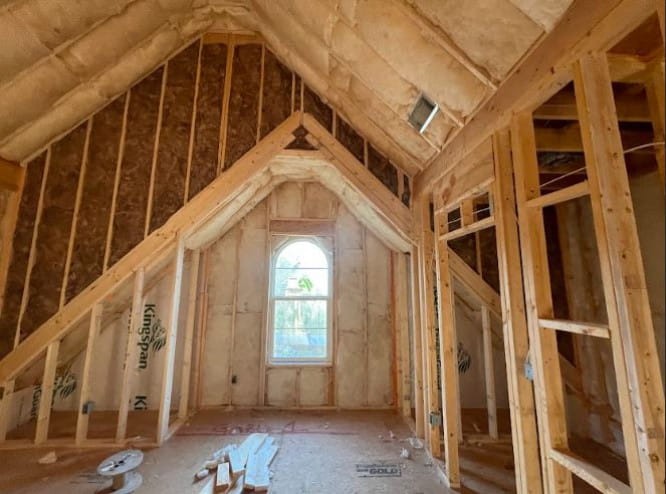

2. Foam board or rigid foam
Foam board or rigid foam offers a more sturdy approach than blanket rolls or batts. You can find foam board and rigid foam in different materials (e.g., polystyrene, polyisocyanurate, polyurethane, and Phenolic) and thicknesses. It is also good for unfinished walls, including foundations, floors, ceilings, and unvented low-slope roofs.
Advantages
- High R-Value
- Strong
- Water-resistant
- Easy to work with
- Permeable to water vapor
Disadvantages
- Not ideal for an already-constructed wall
- Air and moisture leaks are common
- Susceptible to sunlight
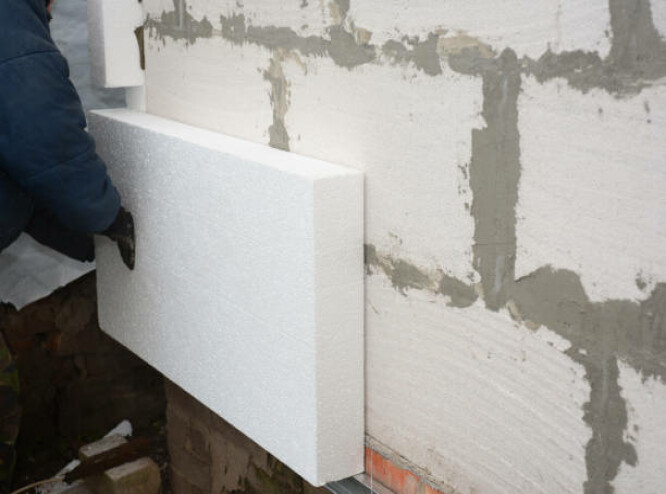

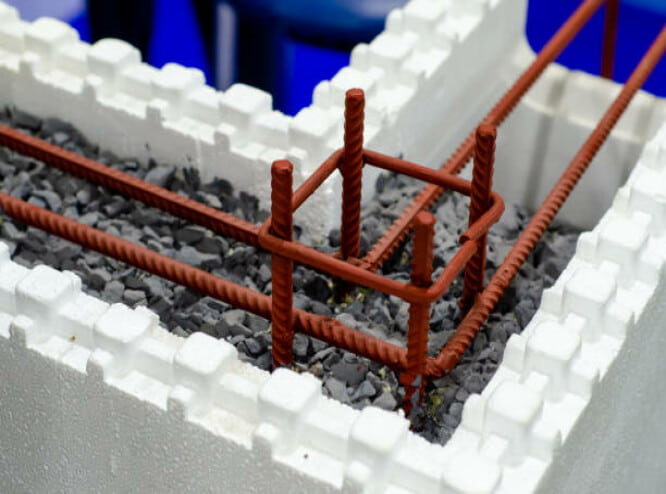
3. Insulated concrete forms (ICF)
Insulated concrete forms are H-shaped structures that consist
of two concrete walls cast between layers of insulation. It looks similar to normally constructed walls, although it is slightly wider. It is often reinforced with steel bars but is filled with more insulation if the wall does not require steel bars. This helps increase the R-Value, making the insulation more effective.
Advantages
- A very durable type of insulation
- Suitable for various
kinds of unfinished walls - Good for noise and temperature control
Disadvantages
- Insulated concrete form insulation is quite expensive
- It is not insect- and water-resistant, so there is the risk of damage by insects and underground water
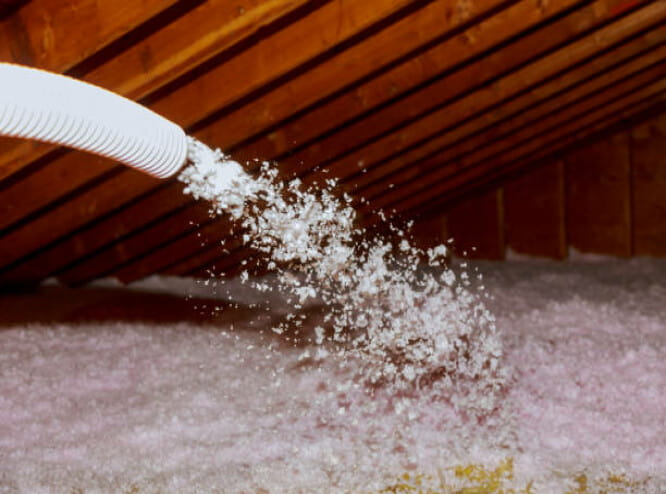
4. Loose-fill or blown-in insulation
This is one of the most common types of insulation being used to date. It is mostly used for enclosing existing walls or wall cavities, like unfinished attic floors or other hard-to-reach places, without disturbing the structure. It consists of tiny material (like confetti) blown into the wall via a hose.
Advantages
- Made of recycled materials and is environmentally friendly
- Very easy to use, especially in areas that are hard to reach or other types of insulation wouldn’t work
Disadvantages
- Although this type of insulation is easy to work with, you will need the services of a professional
- Susceptible to mold if it is not sealed properly

5. Reflective system or radiant barrier insulation
This type of insulation incorporates radiant barriers such as foil-faced kraft paper, plastic film, polyethylene bubbles, or cardboard. These materials work to reflect the heat rather than other insulation types that resist heat. But the reflective surface must face an air space for this type of insulation to be effective.
Advantages
- It is suitable for framing at standard spacing and is a simple type of insulation that can be done individually (do it yourself)
- Reflective system insulation doesn’t deteriorate over time
Disadvantages
- Not effective as a winter insulation material
- Most professionals use this insulation in combination with foam insulation which can incur more cost
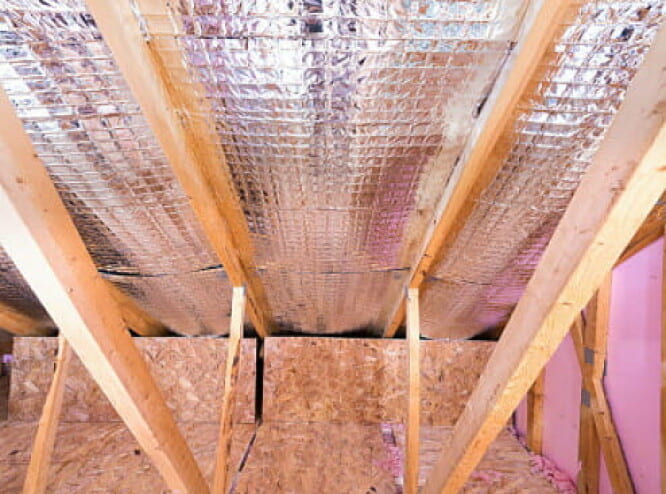

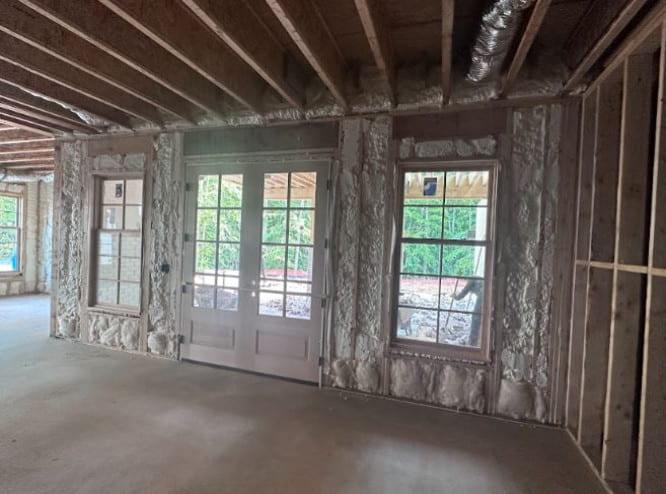
6. Spray foam and foamed-in-place insulation
Spray foam or polyurethane foam (SPF) insulation is a composite material formed when combining isocyanate and polyol resin chemicals. It is sprayed, poured, foamed, or injected as a liquid. Afterward, it expands and hardens to fill the space available. It is often preferred for enclosed areas such as walls, attic surfaces, under floors, or even below a roof.
Advantages
- One of the most effective types of insulation
- It does not require a separate vapor barrier
- Effective for sound control
Disadvantages
- It is not a simple DIY project, and the installation must be done by a professional
- It is not ideal for underground or in-floor insulation

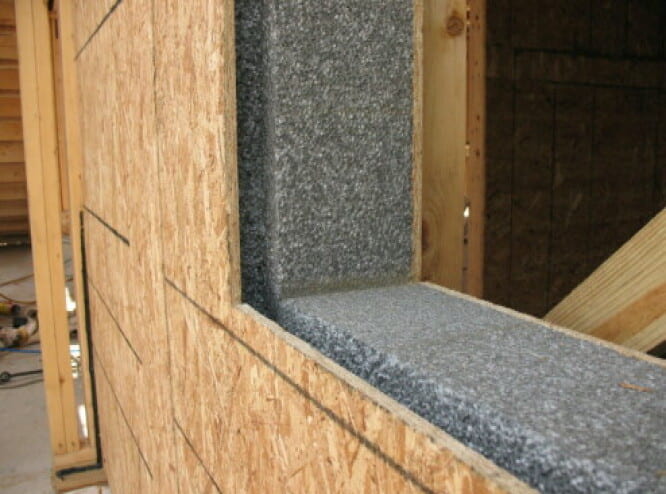
7. Structural insulated panels (SIPS)
This is a high-performance building panel consisting of two rigid board sheathing materials with insulating foam in between the rigid board. The materials in this type of insulation are; foam board or liquid foam insulation core. You can use SIPs for walls, floors, roofs of homes, and light commercial buildings.
Advantages
- SIPs have the highest R-value of all the other types of insulation, making them one of the best
- It also offers superior and uniform insulation compared to all others
Disadvantages
- Structural insulation panels are not insect and pest-proof. Therefore, you will need to lace them with insecticide
- Not really a cost-effective insulation

FAQs
How much does it cost to insulate a house?
The cost of insulating a house depends on the size of the house and the type of insulation you want. But on average, the insulation costs between $1.50 and $5.00 per square foot.
What is the cheapest type of home insulation?
Talking cheapest, Batt and Rolls Insulation is the most inexpensive type of insulation.
What type of home insulation is the most expensive?
The most expensive type of insulation is Spray Foam Insulation.
Conclusion: What is the best type of insulation?
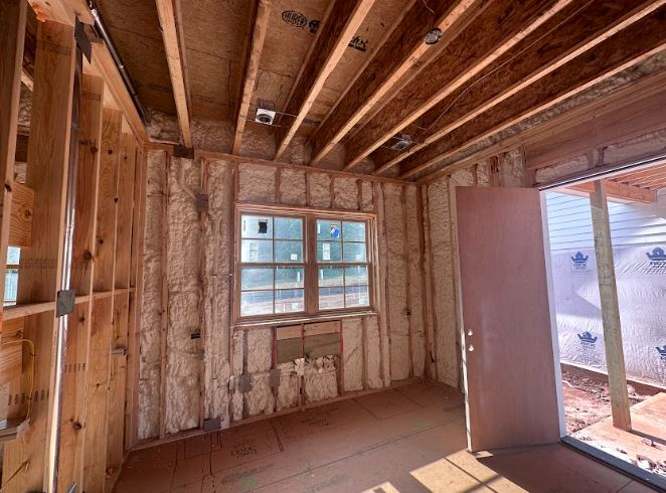

Choosing the best type of insulation is very tough because everybody has different preferences. If you want cheap and affordable insulation, batts and rolls insulation will be a good fit.
On the other hand, if you prefer durable insulation, then Foam Board or Rigid Foam, Spray Foam, and Structural Insulated Panels (SIPS) would be the best choice. This is because this type of insulation has the highest R-value among all the other types of insulation.
I hope you found this article helpful. Before you head out, check out Samkins Construction Lnc today for more articles I believe you will find engaging.
Thanks for reading.
9 thoughts on “Home Insulation – Meaning, Uses, Cost, Types, & Which Is Best”
Comments are closed.